Weight Loss in Early Pregnancy: What’s Normal and What’s Not
In early pregnancy, many women may be concerned about weight loss. Weight loss in early pregnancy is not uncommon, as morning sickness and changes in appetite can lead to a decrease in pounds. Dieting or weight loss during pregnancy is not advised. For your baby’s development, consume a balanced diet and exercise moderately. Too little or too much weight gain during pregnancy is risky. Based on your pre-pregnancy weight and BMI (Body Mass Index), work with your doctor to set a weight-increase range. Eat well, remain active, and gain the necessary weight to give your kid the best start in life and get back to your pre-pregnancy weight thereafter.

Weight Loss in Early Pregnancy: What’s Normal?
First-trimester weight loss is frequent owing to morning sickness and hunger changes. First-trimester weight loss of 5-10 pounds is common and not a reason for worry. Losing more than 10% of your pre-pregnancy weight may indicate that you’re not receiving enough calories or nutrients.
Medical Concerns with Excessive Weight Loss
Weight loss in early pregnancy should be managed under professional medical supervision to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy journey. You may become lacking in nutrients like protein, iron, and folate, which are necessary for your baby’s growth and development.
Significant weight loss also raises your chances of delivering a child with a low birth weight, which may lead to complications after delivery. Whether you have experienced quick or significant weight loss in early pregnancy, inform your doctor immediately so that they can decide whether any treatment or lifestyle changes are required.
How Much Weight Should You Gain?
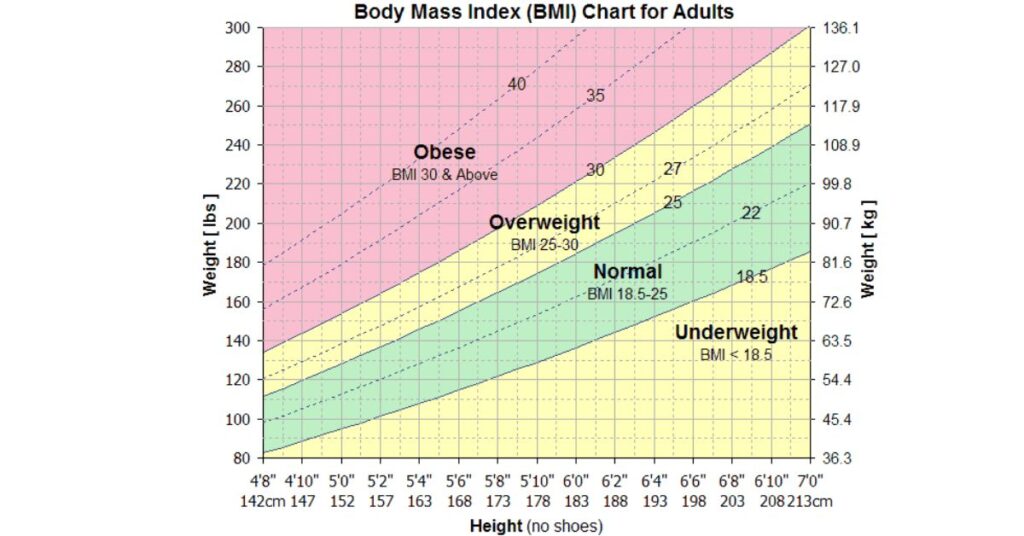
Your pre-pregnancy BMI determines how much weight you should acquire. The Institute of Medicine recommends gaining 25–35 pounds if you were at normal weight before pregnancy. Overweight women should gain 15–25 pounds, whereas underweight women should acquire 28–40 pounds. Proper weight gain protects your baby’s health and growth. Every woman is different, so follow your doctor’s advice depending on her condition. Too much weight gain during pregnancy may cause gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, and delivery problems.
BMI (Body Mass Index) Calculation Chart
Eat a balanced diet, exercise moderately like walking or yoga, and avoid empty calories from junk food and sugary drinks to prevent weight gain. Discuss your weight-gain objectives with your doctor and obtain advice on the proper calories and nutrients for your pre-pregnancy weight and health.
Is It Safe to Lose Weight While Pregnant?
In general, losing weight during pregnancy is not recommended and can be unsafe for you and your baby. Pregnancy is not the time to diet or try to lose weight. However, some weight loss in the first trimester is common and usually not a cause for concern.
Early Pregnancy Weight Loss
Some women experience nausea and food aversions in early pregnancy that can lead to slight weight loss. Losing less than 5–10 pounds in the first trimester typically will not harm the baby. However, if you experience persistent nausea and vomiting and lose more than 10 pounds, you may have a condition called hyperemesis gravidarum. See your doctor right away, as this can lead to dehydration and malnutrition if left untreated.
How Much Weight Should I Gain?
Your pre-pregnancy BMI determines how much weight to acquire. Most women should gain 25–35 pounds. Your baby is in danger if you gain less than 1 to 4 pounds each month in the second and third trimesters.
Dieting and Pregnancy
Strict dieting or trying to lose weight during pregnancy is dangerous and not recommended. Your baby needs the proper nutrition to develop and grow. However, there are some tips to make sure you do not gain too much weight:
Choose a balanced diet with lean proteins, whole grains, fruits and vegetables. Limit excess sugar, fat and empty calories.
Continue to exercise regularly. Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate activity on most days. Walking, swimming or light strength training are good options.
Be very cautious about supplements or herbal products. Many are unsafe during pregnancy and can cause harm. Follow your doctor’s recommendations only when taking prenatal vitamins.
After giving birth, losing 1-2 pounds per week through diet and exercise is considered safe for breastfeeding mothers. However, always talk to your doctor before starting any weight-loss plan. With patience and persistence, you can get back to a healthy weight, but remember: slow and steady wins the race. Stay positive and focus on your new baby!
Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Weight gain during pregnancy is natural and healthy for the mother and fetus. However, prenatal weight increase may affect mother and fetal health. The National Academy of Medicine recommends a 25–35-pound weight gain for those who were normal before pregnancy. If you were underweight, you may need to gain 28 to 40 pounds.
Overweight women should gain 15 to 25 pounds. Obese women may need to gain only 11 to 20 pounds. These are just general guidelines, however, and your doctor will determine an appropriate weight gain target based on your pre-pregnancy weight and body mass index.

Adequate Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet with the proper nutrients is essential for your baby’s growth and development. Focus on lean proteins, dairy, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Staying within your recommended weight gain range means not “eating for two” and avoiding excess calories, sugar and fat. You only need about 300 to 500 extra calories per day in your second and third trimesters.
Reasonable Rate of Gain
Gaining weight at a steady and controlled pace is healthiest for you and your baby. A reasonable rate of gain is about 1 to 2 pounds per week in your second and third trimesters. Losing weight during the first trimester due to morning sickness usually will not hurt your baby, but be sure to stay hydrated and take prenatal vitamins. Your doctor will monitor your weight gain at each visit to make sure you stay within or get back to your target range.
Health Risks
Gaining too much or too little weight during pregnancy poses risks. Excess weight gain increases your chances of gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and complications during delivery. It also makes it more difficult to lose weight after giving birth. Inadequate weight gain can result in a baby that is too small for gestational age and lead to developmental problems. The baby may have health issues and difficulty maintaining body temperature.
After giving birth, focus on recovering and bonding with your baby before worrying about losing weight. Breastfeeding can help with weight loss as it burns extra calories. Once your doctor clears you for exercise, start light activities like walking, swimming or yoga. A balanced diet and moderate exercise will get you back to your pre-pregnancy weight within 6 months to a year. Losing 1 to 2 pounds per week is a safe rate of loss for new mothers.
Risks of Being Overweight While Pregnant
Being overweight or obese during pregnancy might harm you and your kid. Know these hazards so you may take precautions. Weight loss in early pregnancy can be a cause for concern. It’s essential for expectant mothers to maintain a healthy weight and ensure proper nutrition for the growing baby.
High Blood Pressure and Preeclampsia
Weight loss in early pregnancy is a crucial concern for expectant mothers. Obesity strains the heart and blood arteries, increasing the risk of gestational hypertension. Preeclampsia, which causes high blood pressure and protein in the urine, may result. Both conditions may require early delivery and bed rest. Losing weight before pregnancy and gaining the recommended amount during pregnancy can help lower these risks.
Gestational Diabetes
Extra weight also increases your risk of gestational diabetes, which is high blood sugar that develops during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes requires treatment and diet changes to be controlled and can have complications for your baby. Shedding excess pounds before conceiving and limiting weight gain during pregnancy can decrease your risk.
Sleep Apnea
Being overweight or obese also raises your risk of developing sleep apnea during pregnancy, where your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. Sleep apnea deprives you and your baby of oxygen and can cause complications. Losing weight is the most effective way to relieve sleep apnea and its risks.
Labor and Delivery Complications
Excess weight may lead to complications during labor and delivery, including failed induction, longer labor, and an increased risk of cesarean section (C-section). It can also cause challenges with anesthesia and make surgery more difficult if a C-section becomes necessary. Losing weight before pregnancy and gaining weight within recommended guidelines during pregnancy can help minimize these complications.
Weight Retention After Pregnancy
Women who are overweight or obese before pregnancy are more likely to retain extra weight after giving birth. Excess postpartum weight is associated with long-term health issues like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Focusing on diet and exercise to reach a healthy weight before pregnancy and limiting weight gain during pregnancy can make it easier to return to your pre-pregnancy weight after delivery.
Being overweight during pregnancy has several dangers, but many may be avoided with weight reduction before conception and appropriate weight gain throughout pregnancy. Putting your and your baby’s health first will ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery. The rewards of your efforts will last well beyond your pregnancy.
Safely Losing Weight After Giving Birth
It is normal for new mothers to desire to regain their pre-pregnancy weight following childbirth. However, doing so progressively and securely is essential. Rapid weight loss following childbirth can be hazardous for both the mother and the infant.
Breastfeeding
If you are breastfeeding, focus on eating a healthy diet with plenty of nutrients. Breastfeeding alone burns around 500 calories per day, so many women lose weight naturally while breastfeeding. You should aim to lose about 1-2 pounds per week. Losing weight at a moderate pace will not affect your milk supply or the nutrition your baby receives.
Diet and Exercise
Your doctor will clear you to exercise 6 weeks after a vaginal delivery or 8 weeks after a C-section. You may start walking, swimming, or yoga. Spend time building strength and endurance. The diet should include lean meats, fruits, vegetables, entire grains, and healthy fats. Hydrate and eat every couple of hours to stay energized. Weight reduction should be gradual, 1-2 pounds each week.
Be Realistic
Keep in mind that it took 9 months to gain the weight, so losing it at a moderate pace will take time. Most women can lose their baby weight in 6–12 months with a healthy diet and exercise alone. Every woman’s body is different, so try not to compare yourself to unrealistic societal pressures. Focus on listening to your body and talk to your doctor if you have concerns about your weight loss timeline or methods.
Supplements and Fad Diets
Avoid any supplements, diet pills or fad diets while breastfeeding. These methods are unsafe and can contaminate your breast milk. The healthiest way to lose weight after pregnancy is through nutritious eating and moderate exercise. Trust that your body will return to a healthy weight when the time is right.
Losing weight after pregnancy requires patience and self-care. Focus on nourishing yourself and your baby, move your body when you are ready and the weight will come off over time. Every woman’s journey is different, so be gentle with yourself and celebrate your amazing accomplishments. With love and support, you will get to a place where you feel comfortable and confident in your new body.
Conclusion
While it’s common to shed a few pounds in the early stages of pregnancy, this is completely natural and shouldn’t be a reason for alarm. Eat a healthy, well-rounded diet that provides lots of nutrients to help your baby grow and thrive. Both you and your unborn child are in danger if your weight gain is excessive or inadequate.
Never put off seeing a doctor about your worries about your weight, whether you’re gaining or losing. They can evaluate your specific situation, provide guidance, and help put you at ease. Pregnancy is a journey, so do your best to embrace this special time and take good care of yourself. In doing so, you’ll be giving your baby the best start in life.